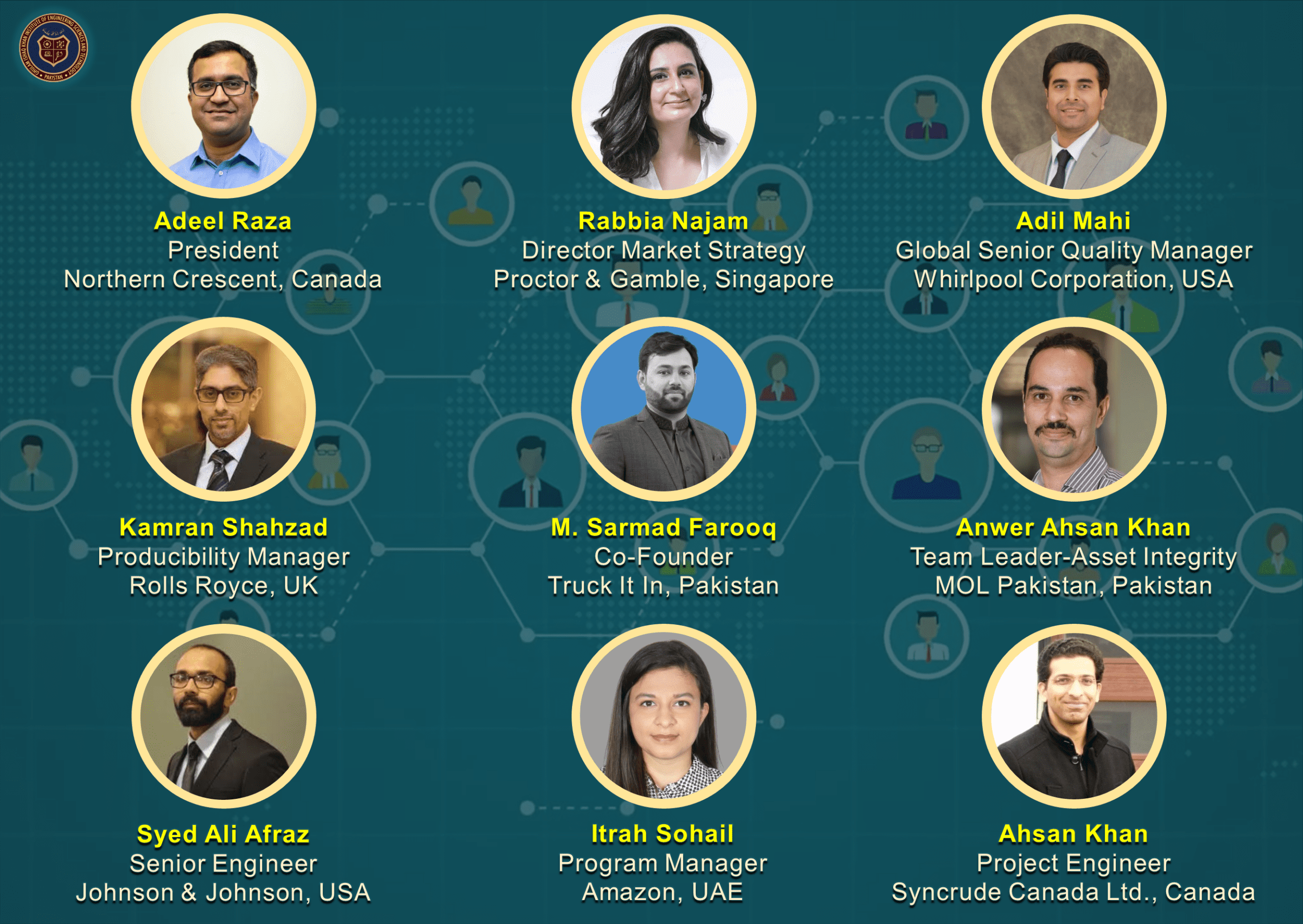
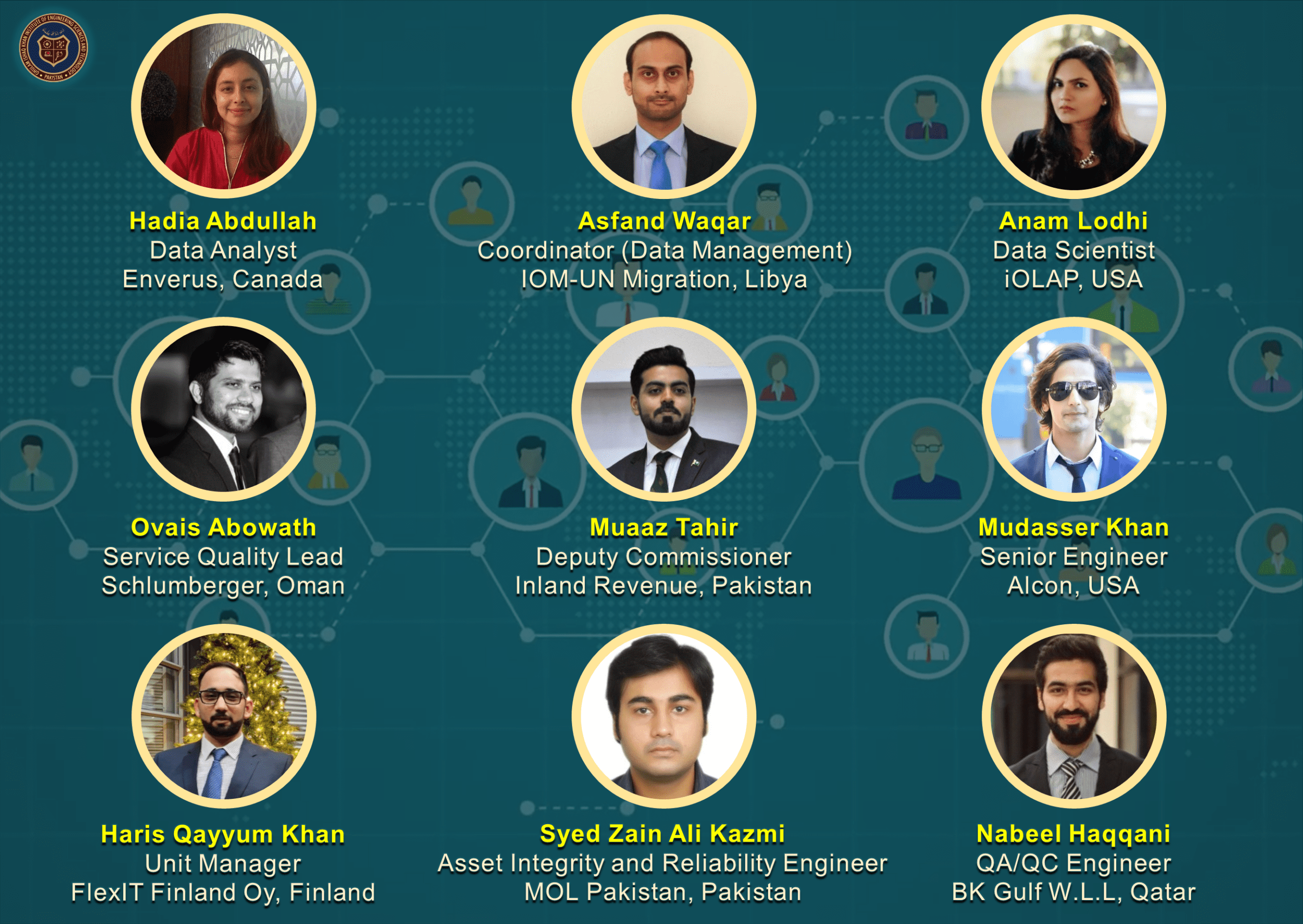
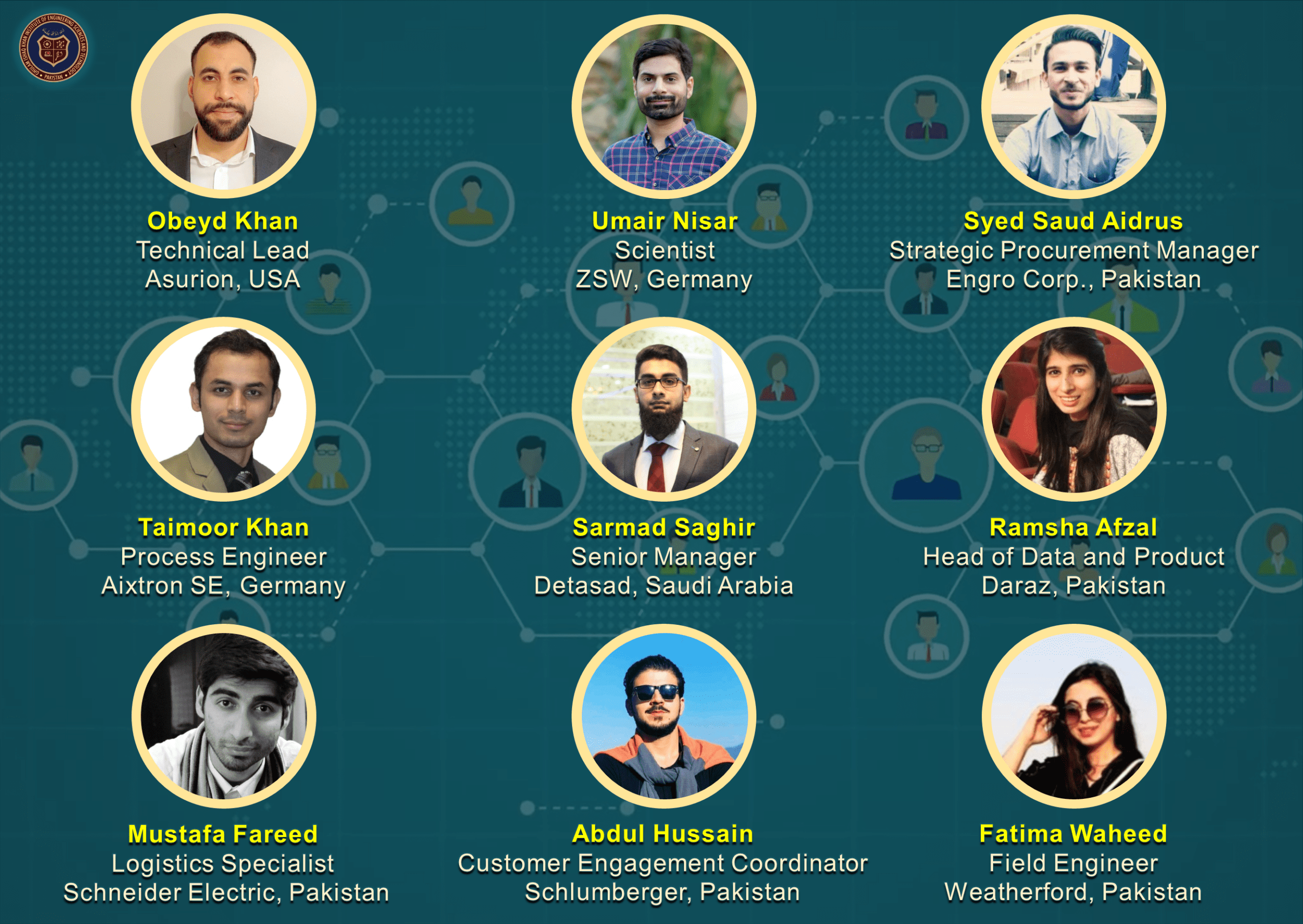
NOTABLE ORGANIZATIONS DMSE ALUMNI ARE WORKING AT



WELCOME TO THE ‘WORLD OF MATERIALS’
Modern trends in the scientific and technological race require innovative solutions to complex issues being faced by the world at large. Scientists and experts from various fields including physics, chemistry, biology, engineering etc. are joining hands to utilize the knowledge and understanding of Materials Science and Engineering for expediting scientific breakthroughs and proposing real-time engineering solutions. At the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, we offer a high-quality, impactful and world-class PEC accredited program in Materials Engineering with the goal to produce graduates that are expected to excel in both industry and academia at national and international fronts. We prepare graduates that are sound theoretically and technically along with having excellent soft skills required for various professional contexts. Since the inception of GIK Institute, and in-line with the vision of Dr. A. Q. Khan, the Materials Engineering program has produced 750+ graduates now successfully contributing to a variety of industrial, research, business, and academic ventures.
DID YOU KNOW?
- Our BS in Materials Engineering Program is Accredited by PEC, HEC and Washignton Accord.
- Materials Engineering graduates are working in a variety of national and international organizations (see Our Graduates and companies list).
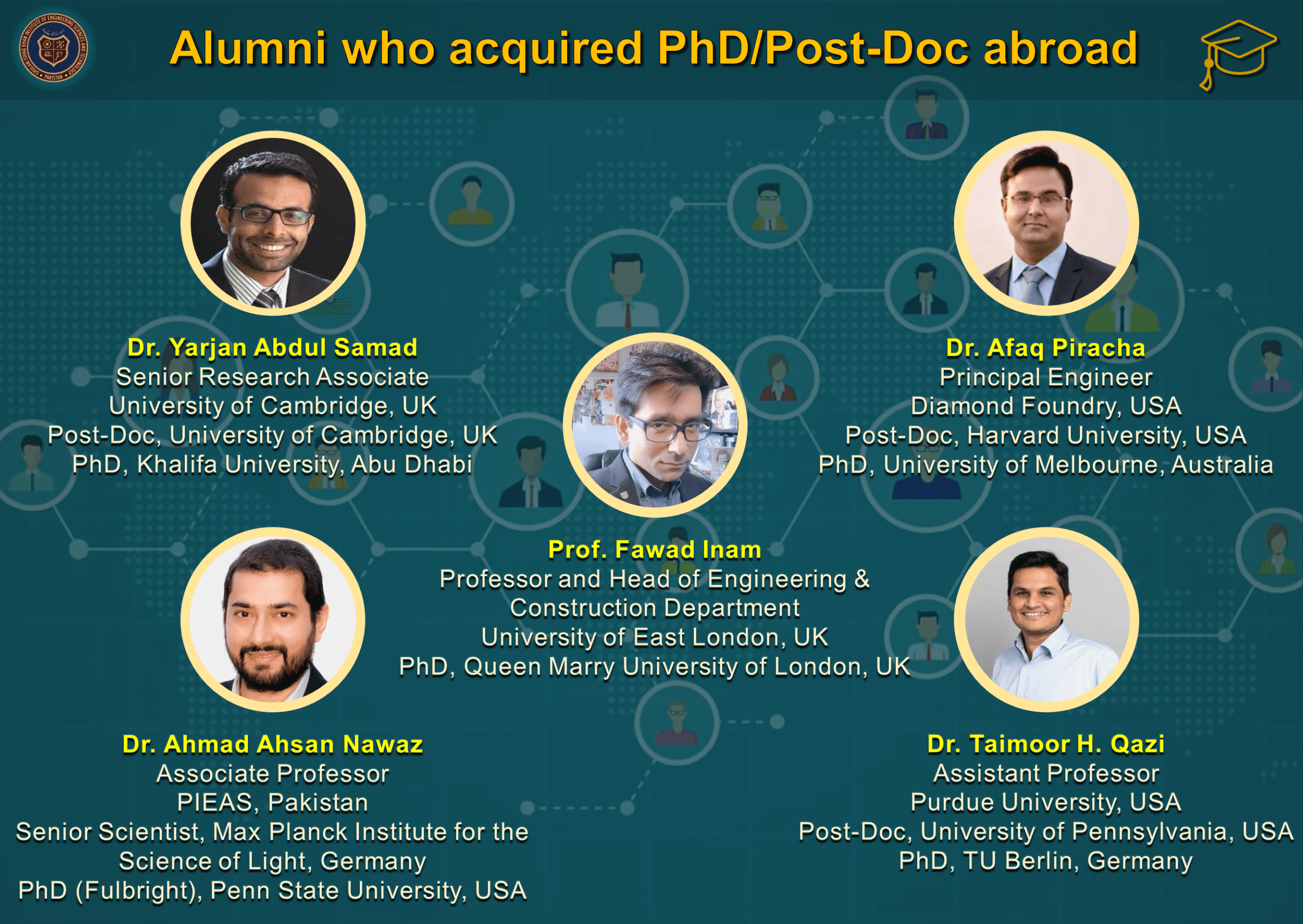
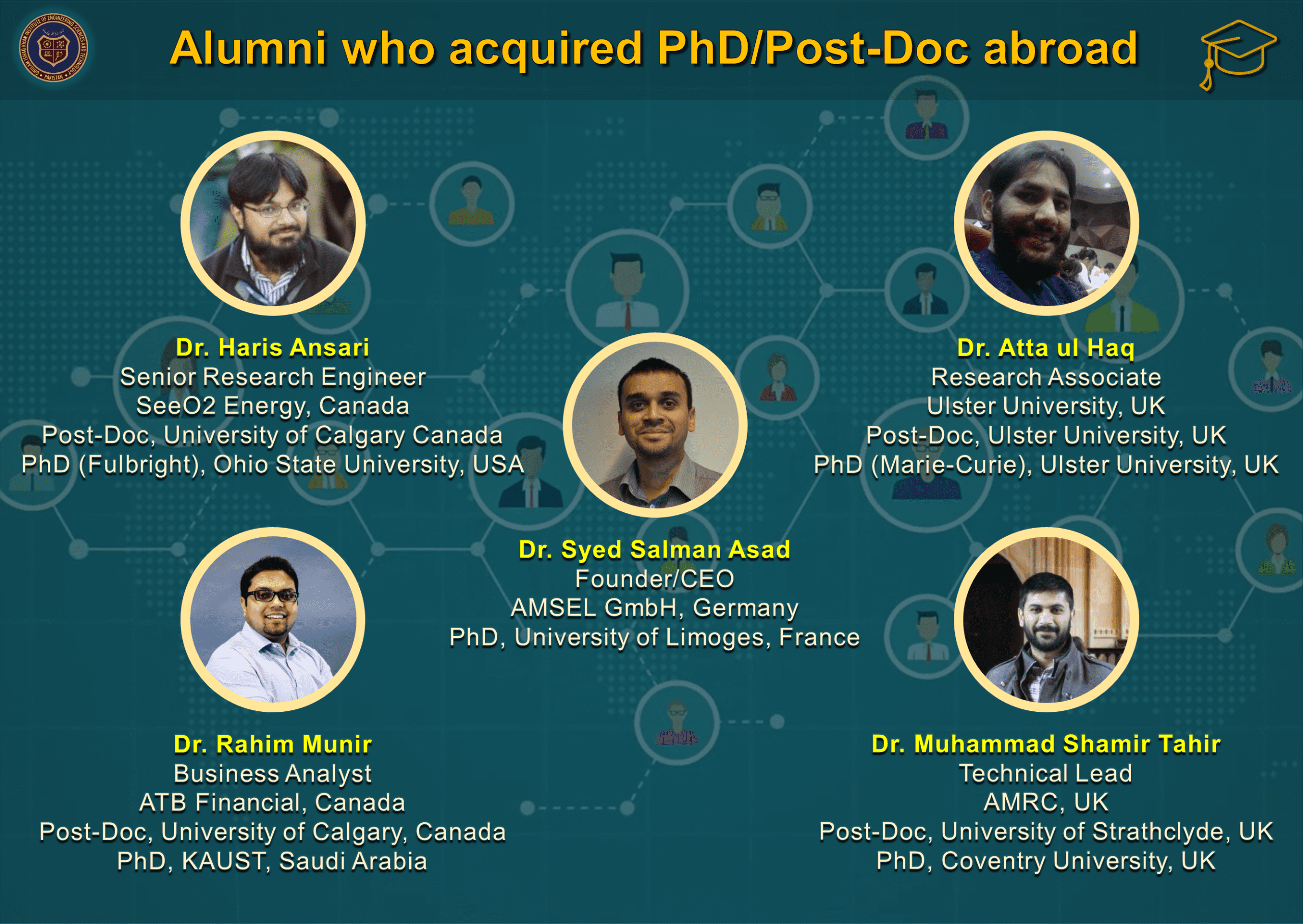
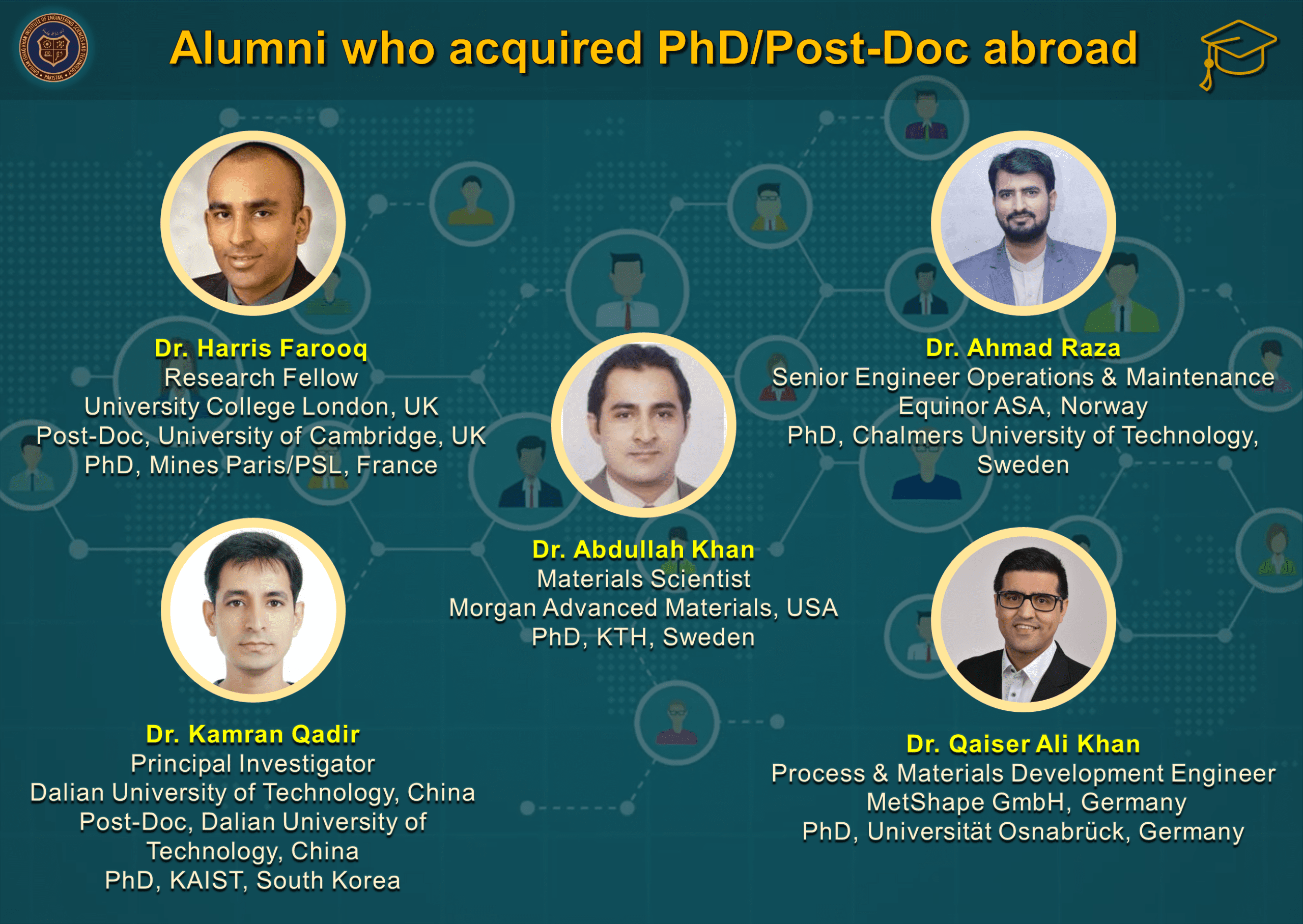
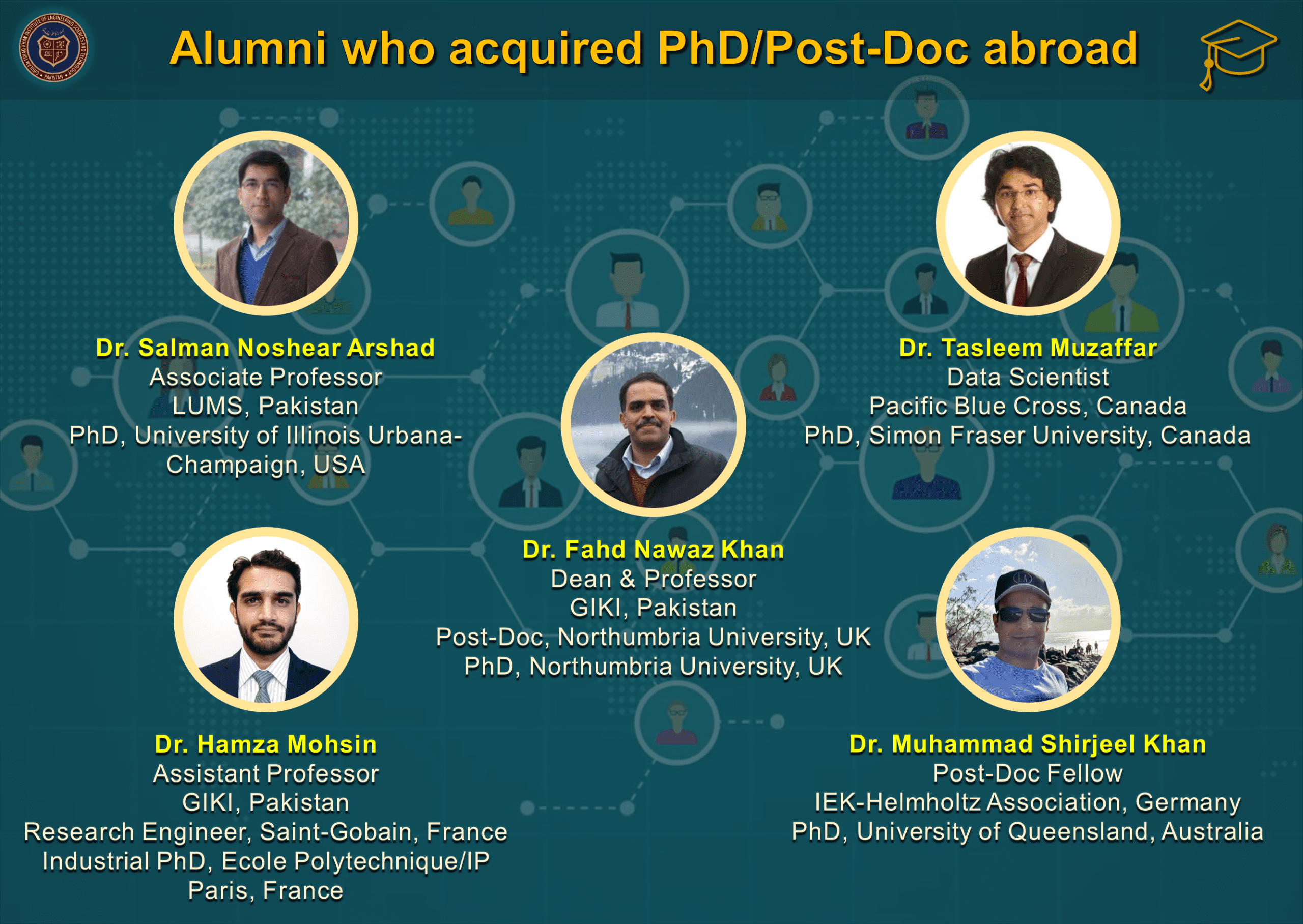
- Materials Engineering graduates have secured fully-funded Master and PhD admissions in world’s top 50 Universities and are currently serving academia, research & development multinationals and other reputable organizations around the globe (see Our Graduates).
- Materials Engineering is at the heart of international innovation in science and technology with relevant programs being offered in almost all the top 100 universities in the world including MIT, Stanford, Harvard, Oxford, Cambridge etc.
- A degree in Materials Engineering is the gateway to fully-funded Master programs in world’s top universities and international careers in research and development.

The memories of my admission into GIK Institute back in 1996 are always fresh in my mind. I was a young lad like you, looking into the details of what Materials Science and Engineering was all about, and decided to give it a shot considering the global scientific trends. Having been connected to the department and the field for 25 years, I must admit that the discipline around the globe has come a long way and my decision of becoming a Materials Engineer is proving to be the right choice every passing day. Technological advancements have made it essential to know, understand, research and improve the properties of materials along with producing break through inventions in the form of new materials, for instance, graphene, that have changed even the fundamentals of science. Thanks to advancements in Materials Science and Engineering, humanity has been able to manufacture devices at the nanoscale of which a smart watch is a perfect example. Modern flexible electronic devices employing stretchable screens and electronics, NASA’s space shuttles resisting extreme space environment, temperature sensor and body components of Mars Curiosity Rover, Beryllium mirror in James Webb Telescope to explore the universe, solar cells employing semiconductors, lithium-ion batteries employed in smartphones and electric vehicles, biomedical implants in the form of heart stents or dental braces are a few examples of how Materials Engineering has shaped the scientific community.
Our graduates have excelled as a result of the training they receive here and are currently involved as senior members in multinational FMCG organizations, founders of start-ups and, most-importantly, scientists in R&D organizations as well as professors in academic institutes worldwide. We inculcate in our graduates the qualities to adapt to whatever career they would like to pursue. So, come join us for our degree program and become of a part of the community shaping the world of today and tomorrow.
Prof. Dr. Fahd Nawaz Khan
Dean & Alumnus (Class of 2000)
Faculty of Materials and Chemical Engineering

 mohajir@giki.edu.pk (Mr. Mohajir Shah, PS to Dean)
mohajir@giki.edu.pk (Mr. Mohajir Shah, PS to Dean)
If you would like to know more about the Materials Engineering Program, its requirements, scholarships, and resulting career options, please drop us an email. You will be connected to the most relevant person in the Faculty. You may also follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram and Twitter for news and updates.
 https://www.linkedin.com/company/dmsegiki/
https://www.linkedin.com/company/dmsegiki/
 https://www.facebook.com/Msegiki
https://www.facebook.com/Msegiki
 https://www.instagram.com/dmsegiki/
https://www.instagram.com/dmsegiki/